Oligo secondary structure
The oligo secondary structure refers to a three-dimensional form of a local segment of nucleic acids. An oligo secondary structure is produced by intermolecular or intramolecular interaction. The presence of the oligo structure can hinder its binding to the target sequence, thus leading to reduced or no yield of the product. The likelihood of secondary structure formation can differ greatly depending on the oligo sequence.
The stability of the secondary structure is represented as deltaG (ΔG), the energy required to break the secondary structure. The more negative the ΔG, the more stable and undesirable the secondary structure is.
Hairpin
The hairpin structure forms if the oligo is complementary to itself.
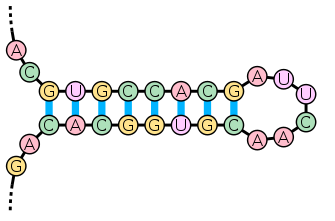
Figure 1. Hairpin structure.
Dimer
The dimer structure forms by intermolecular interaction between two oligos.