Risk calculation for x-linked dominant inheritance
In this rare mode of inheritance the disease gene is located on the X chromosome, and both men and women carrying the disease-causing mutation will develop the disease. The risk of the offspring will depend on the sex of the affected parent as well as the sex of the child: an affected man will pass on the X chromosome with the mutation to all of his daughters but none of his sons, meaning that disease risk in daughters is 100% and in sons 0%; an affected woman will have a 50% risk of passing on the mutation and the disease to both daughters and sons.
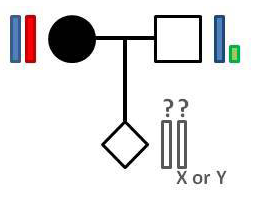
Figure 1. A pedigree showing x-linked dominant inheritance with the mother carrying the disease-causing mutation.
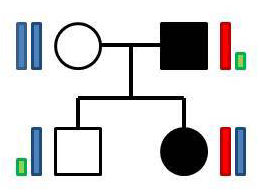
Figure 2. A pedigree showing x-linked dominant inheritance with the father carrying the disease-causing mutation.